18A200
Urate Lowering Therapy (ULT) reduces Plasma Homocysteine Levels: a Potential mechanism for Cardiovascular Risk Disease Modification.
Author(s)
Yousef Alammari, Diana Gheta, David Kane, Gerard Boran*, Ronan H Mullan
Department(s)/Institutions
Department of Rheumatology & Department of Clinical Chemistry*, Tallaght University Hospital, Dublin 24
Introduction
Hyperuricaemia is a risk factor for gout, cardiovascular disease (CVD), Type 2 Diabetes (T2DM) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Plasma homocysteine levels are elevated in gout and correlate with serum uric acid levels. The associations of elevated plasma homocysteine levels with disease progression in CKD, CVD and T2DM are also well documented, indicating potential overlapping mechanisms of disease involving both monosodium urate (MSU) and homocysteine (1-4).
Aims/Background
This case-control study evaluated the effect of ULT on cardiovascular risk factors in hyperuricaemic individuals.
Method
Hyperuricaemic cases with foot pain +/- ultrasound evidence of early gout (n=16) were compared with asymptomatic hyperuricaemic controls (n=15). Cases were treated with febuxostat 80mg for 3 months. Serum urate, ESR, CRP, fasting homocysteine, glucose, insulin and lipid levels were measured at 0-3 months.
Results
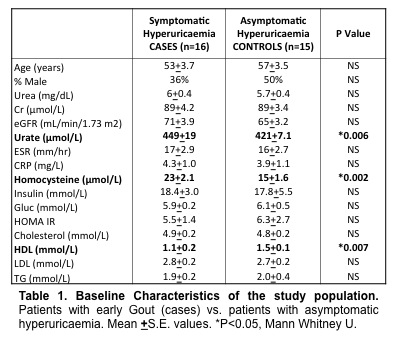
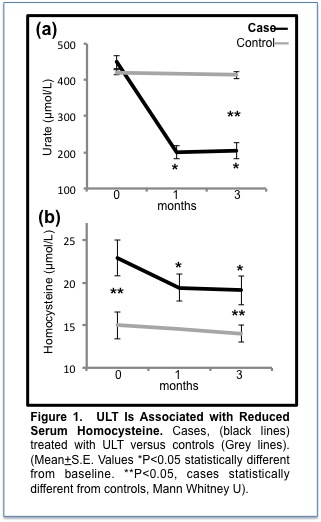
Cases had higher levels of baseline serum urate than asymptomatic controls (449+19 μmol/L vs. 421+7.1 controls; P=0.006), higher levels of homocysteine (23+2.1μmol/L vs. 15+1.6 controls; P=0.002) and lower levels of HDL cholesterol (1.1+0.2 mmol/L vs. 1.5+0.1 controls; P=0.007) (Table 1). ULT reduced serum homocysteine at 1-month (19+1.6 μmol/L; P=0.001) and 3-months (19+1.7 μmol/L; P=0.002). The change in homocysteine at 3-months correlated with the change in serum urate (r=0.394, P=0.05) but not ESR, CRP, lipids or measures of insulin resistance. No significant changes in insulin resistance, ESR, CRP or lipid measurements following ULT were observed.
Conclusions
Elevated levels of plasma homocysteine are reduced following ULT, a novel and previously unpublished finding. Changes in plasma homocysteine correlate with changes in serum urate after ULT. The known cardiovascular benefits of ULT including the amelioration CKD disease progression may be mediated in part through homocysteine effects. A full elucidation of the pathological effects of metabolic intermediates including homocysteine and MSU may lead to the development of future treatment strategies for the systemic complications of inflammatory metabolic diseases